Overview
The Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) is a tiny chip with an outsized job. It proves who you are to a mobile network, lets your device connect securely, and unlocks services such as voice calls, messaging, data, and even mobile payments. Together, the data stored on the SIM and the systems that manage it form the “SIM Information System.” This ecosystem is central to modern telecommunications and is evolving fast as we move into the era of eSIM, iSIM, 5G, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
What SIM Information Actually Is
A SIM contains key data that allows a device to connect to a mobile network:
- A unique subscriber identifier (such as IMSI) that represents you to the network
- Authentication and encryption keys used to verify and protect your connection
- Operator and network settings, such as preferred networks and service configurations
- Optional applets for services like mobile payments or carrier tools
Think of it as a secure ID card plus a key, built into your phone or wearable, that the network trusts.
How SIM Technology Evolved
SIMs have changed a lot since the early plastic cards:
- Full-size to mini, micro, and nano SIM: Smaller cards to fit slimmer devices
- eSIM (embedded SIM): A chip built into the device; profiles are downloaded digitally instead of swapping plastic cards
- iSIM (integrated SIM): SIM functions integrated directly into the device’s main chipset, saving space and power
- Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP): Enables carriers to add, remove, or update SIM profiles over the air
This evolution makes activation faster, switching carriers easier, and large-scale device management (like for IoT) more practical.
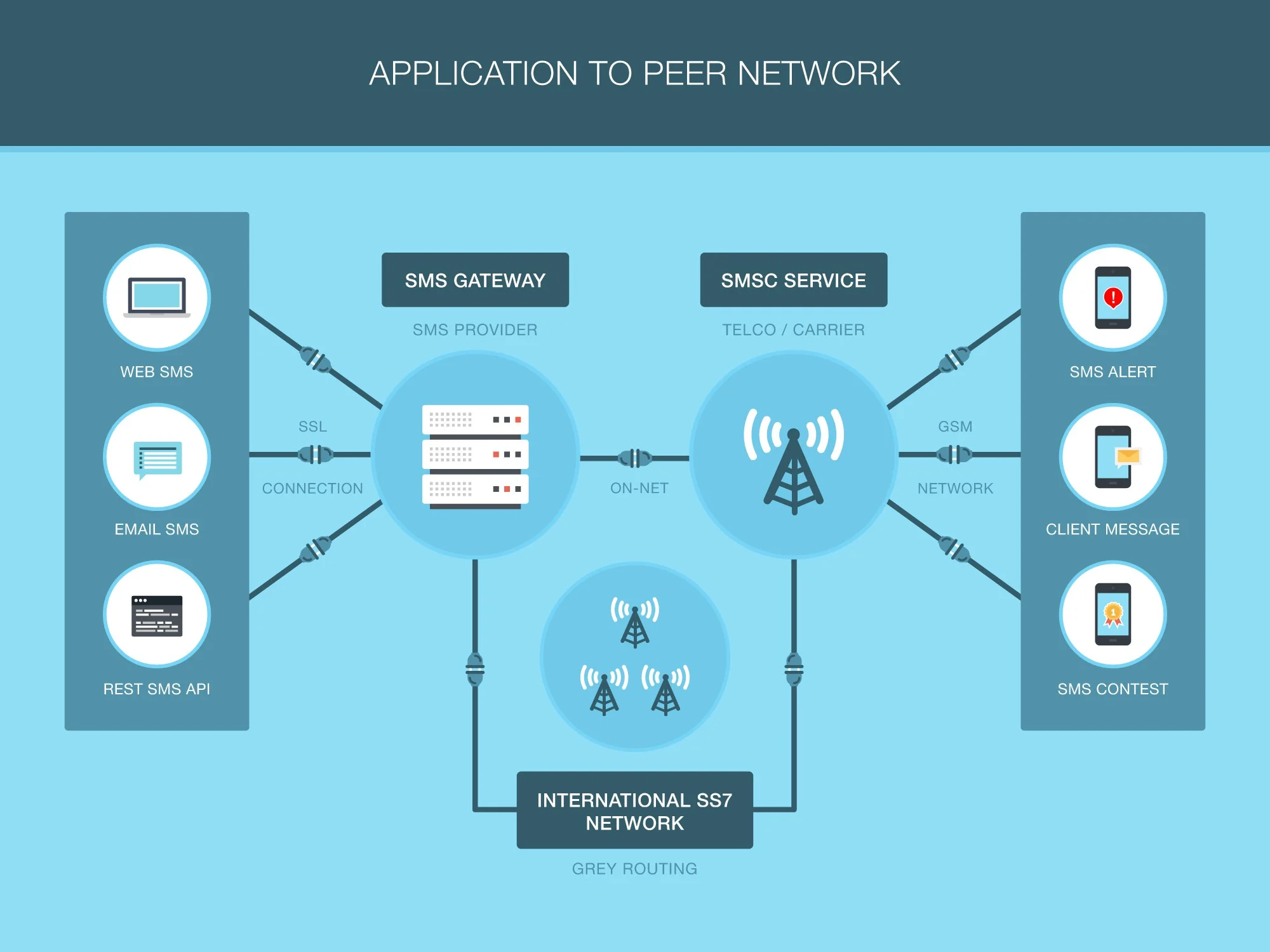
Core Components of a SIM Information System
A complete system includes:
- The SIM or eSIM/iSIM on the device
- Carrier databases (like HLR/HSS/UDM) that store subscriber profiles
- Authentication servers and security keys
- Provisioning platforms to activate, suspend, or update service
- Customer care and compliance systems for registration and lawful use
Role of SIMs in Everyday Mobile Communication
- Network access: Connects your device to 2G/3G/4G/5G networks
- Security: Uses cryptographic checks so only authorized devices connect
- Roaming: Lets you use partner networks abroad
- Services: Enables voice, SMS, data, VoLTE/VoWiFi, and sometimes value‑added services
- Identity and payments: Can back secure elements and certain verification flows
SIM Registration and Why It Matters
Many countries require SIM registration (KYC) to link SIMs to real identities. This can help:
- Reduce fraud and misuse (e.g., anonymous scams)
- Support emergency response and lawful investigations
- Improve data accuracy for operators
Registration practices vary by country and may be tied to national ID systems. The goal is to balance safety with privacy rights and due process.
Security Measures That Protect SIM Information
- Strong authentication: Mutual verification between device and network
- Encryption: Protects traffic and sensitive keys
- PIN/PUK: Prevents unauthorized use if a SIM is removed from a device
- Secure applets and firmware: Prevent tampering and unauthorized code
- Over-the-air updates: Patch vulnerabilities and update profiles securely
- Access controls and audits: Limit who inside an organization can view or change subscriber data
Benefits of a Robust SIM Information System
- Safer connections: Lower risk of impersonation or eavesdropping
- Seamless activation: eSIM lets you scan a QR code and go live quickly
- Flexible service: Add or switch plans without visiting a store
- Better device management: Essential for fleets and IoT deployments
- Trust and reliability: Clear records and controls reduce errors and downtime
Challenges and Risks to Watch
- SIM swap fraud: Attackers trick providers into porting your number to their SIM, then intercept codes and accounts
- Cloning and theft: Rare but possible with weak controls or social engineering
- Data privacy: Storing identity and usage data requires strong protection and strict access policies
- Regulatory complexity: Different countries impose different rules for registration, retention, and lawful intercept
- Fragmented experiences: Not all devices or carriers support eSIM/iSIM in the same way
Practical Tips for Users
- Use a SIM PIN and keep your PUK secure
- Enable account-level protections with your carrier (port-out PIN, extra verification)
- Favor app-based two-factor authentication (like authenticator apps) over SMS where possible
- Keep your device OS updated to benefit from security patches
- If you change devices or plans, wipe old profiles you no longer need
Future Trends and What They Mean
- eSIM and iSIM everywhere: Lighter devices, faster onboarding, fewer plastic cards
- IoT at scale: Billions of sensors and machines connecting with remotely managed profiles
- Smarter networks: 5G network slicing and private networks will rely on precise, secure identity via SIM-like credentials
- Better user control: Clearer transparency dashboards, data minimization, and consent-based sharing
- Stronger defenses: Wider adoption of anti‑SIM‑swap controls and continuous authentication methods
Impact on the Telecom Industry
- Faster onboarding: Digital activation cuts costs and improves customer experience
- New services: Flexible profiles enable travel eSIMs, temporary plans, and cross-border IoT
- Operational resilience: Centralized provisioning and analytics improve reliability
- Security posture: Industry-wide push to reduce fraud and protect identities
- Ecosystem growth: Easier connectivity fuels fintech, healthtech, smart cities, and more
Case Snapshots (Illustrative)
- National SIM registration: Countries tying SIMs to verified IDs reported reductions in anonymous fraud, alongside heightened privacy expectations and oversight needs
- Enterprise eSIM rollout: A logistics firm deploys eSIM wearables to drivers, enabling instant replacements and remote plan changes, reducing downtime
- SIM swap incident: A user’s number is ported by attackers; carrier introduces stricter identity checks and port-out PINs, cutting repeat cases
Public Perception and Trust
Trust depends on clarity and control. Users want to know what is collected, why, for how long, and who can access it. Carriers that publish transparent policies, offer easy privacy controls, notify users about changes, and provide quick help after incidents build stronger relationships.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Rules usually cover:
- SIM registration and identity verification (KYC)
- Data protection and retention limits
- Number portability and dispute resolution
- Lawful intercept under due legal process
- Transparency and user rights (access, correction, deletion where applicable)
Compliance protects users and keeps telecom markets fair and secure.
FAQs
What exactly is SIM information?
It’s the secure data on your SIM (or eSIM/iSIM) plus the carrier systems that authenticate you, enable services, and keep your connection safe.
Why is SIM registration important?
It links SIMs to verified identities, which helps reduce abuse of mobile services and supports safety, while requiring strong privacy protections.
How does SIM information improve network security?
It enables cryptographic authentication, ensures only valid devices connect, and supports encryption of communications and updates.
What are the main risks?
SIM swap fraud, social engineering, and data misuse. Strong authentication, carrier-level protections, and user awareness reduce these risks.
How is SIM tech evolving?
From plastic SIMs to eSIM and iSIM with remote provisioning, tighter security, and easier switching, especially valuable for IoT and 5G use cases.
Conclusion
The SIM Information System is the quiet foundation of mobile life. It proves your identity, secures your connection, and powers everything from calls and messages to streaming and payments. As SIMs move from plastic cards to embedded and integrated forms, activation becomes simpler, devices get smaller, and networks become smarter. The path forward is clear: keep security strong, respect privacy, comply with fair regulations, and give users control. Do that well, and SIM technology will continue to deliver safe, seamless connectivity for people, businesses, and the billions of devices joining the network every day.

 SIM OWNER DETAILS
SIM OWNER DETAILS